1 Array List
Coding
Java
Data Structure
Array List
This lecture introduces the basic concepts of array and ArrayList in Java.
Array Review
Definitions
- Array: sequenced collection of variables all of the same type.
- Element: each value stored in an array.
- Array length: maximum number of elements that can be stored in the array.
- Index: uniquely refers to each element. Range: 0, 1, 2, …, length-1.
Array vs. ArrayList in Java
- Array declaration
int[] myArray = {1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9};
int[] myArray new int[10];
Car[] myArray new Car[6];
// Illegal:
// int[] myArray = new int[];- Array must be initialized with a fixed length.
- ArrayList declaration
ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Car> myList = new ArrayList<Car>();
ArrayList<Car> myList = new ArrayList<Car>(6);- Set an item to a value: time complexity = \(\mathcal{O}(1)\).
// Array:
myArray[4] = 30; // set item at index 4 to 30.
// ArrayList:
myList.set(4, 30);- Get the value of an item: time complexity = \(\mathcal{O}(1)\).
x = myArray[4]; // get item value at index 4.
myList.get(4);Implementing ArrayList
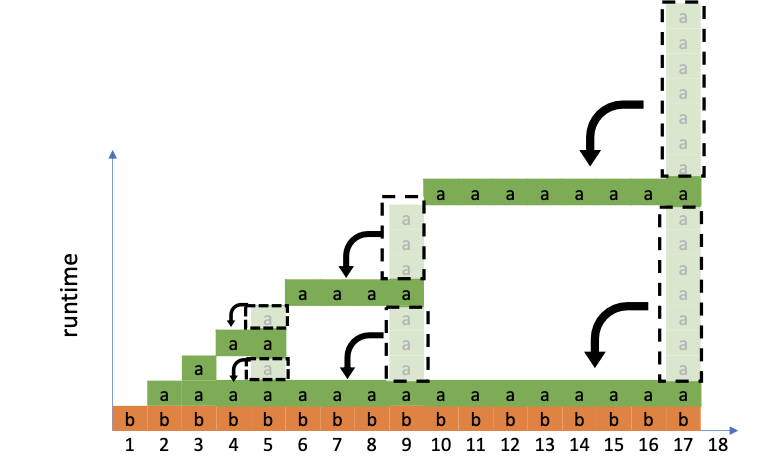
- Time complexity analysis:
Add a new element at an index in ArrayList = \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
Remove an element at an index in ArrayList = \(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
Push an element to the end of ArrayList = \(\mathcal{O}(1)\). (No matter in the dynamic sized case or fixed sized case.)