Polynomial Representation of Arnoldi
Arnoldi’s Method Overview
Find \(q_1,\dots,q_n\), orthonormal basis, of the Krylov subspace \(\mathcal{K}_n(A,b)=\sp\qty{b,Ab,A^2b,\dots,A^{n-1}b}\).
- Arnoldi relation: \[ AQ_n=Q_{n+1}H_n, \] where \(Q_n=\mqty[q_1&\dots&q_n]\) and \(H_n\) is an upper Hessenberg matrix.
By construction of \(Q_n\), we know that \(Q_ny\in\mathcal{K}_n(A,b)\). If we jump to the next iteration, we add \(A^nb\) to the Krylov subspace, and so we want to find \(q_{n+1}\) such that \[ q_{n+1}\perp \mathcal{K}_n(A,b)\cup\{A^nb\}. \]
That is, we want to minimize the distance between \(A^nb\) and the Krylov subspace. Visually, we have the following: 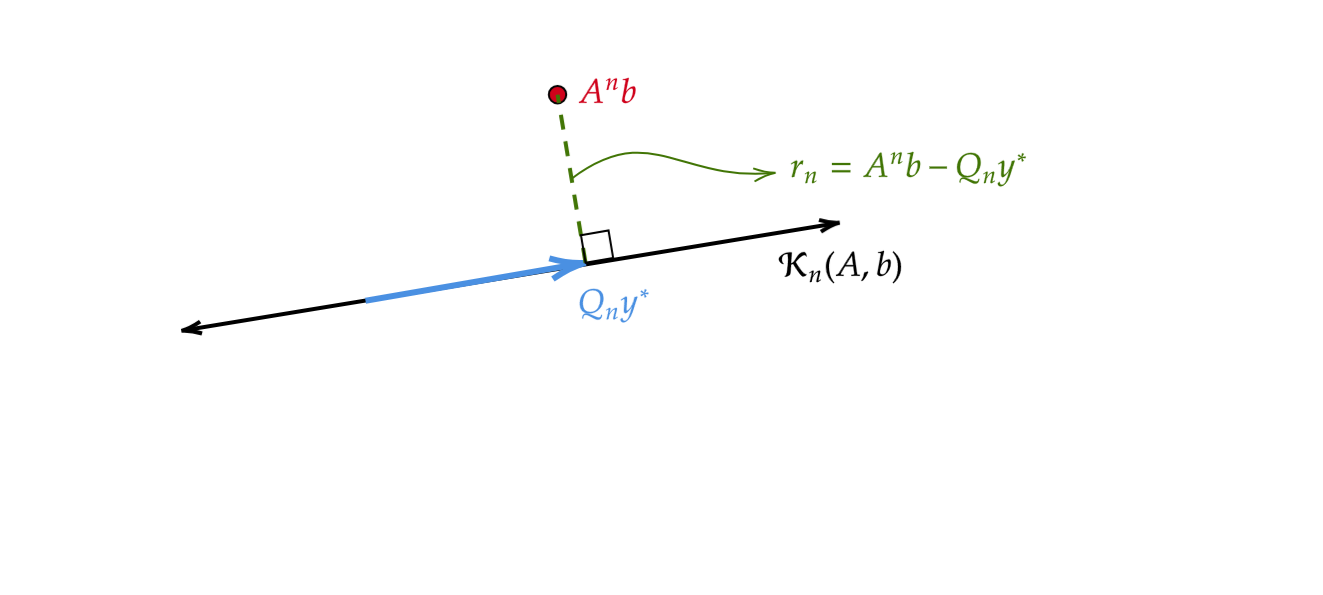
Set Up an Optimization Problem
As \(Q_ny\in\mathcal{K}_n(A,b)\), we can rewrite the problem as minimizing the residual \(r_n=A^nb-Q_ny\): \[ \min_{y\in\C^n}\|r_n\|=\min_{y\in\mathbb{C}^n}\norm{A^nb-Q_ny}_2. \tag{Arnoldi Approx.} \]
Polynomial Representation
As \(Q_ny\in\mathcal{K}_n(A,b)=\sp\qty{b,Ab,A^2b,\dots,A^{n-1}b}\), we can rewrite \(Q_ny\) as linear combinations of \(b,Ab,A^2b,\dots,A^{n-1}b\): \[ Q_ny=y_1b+y_2Ab+\dots+y_nA^{n-1}b \]
Plug-in this into (Arnoldi Approx.), we get \[ \begin{aligned} \min_{y\in\C^n}\|r_n\|&=\min_{y\in\C^n}\norm{A^nb-Q_ny}_2\\ &=\min_{y\in\C^n}\norm{A^nb-\qty(y_1b+y_2Ab+\dots+y_nA^{n-1}b)}_2\\ &=\min_{y\in\C^n}\norm{A^nb-y_1b-y_2Ab-\dots-y_nA^{n-1}b}_2\\ &=\min_{y\in\C^n}\norm{-y_1b-y_2Ab-\dots-y_nA^{n-1}b+A^nb}_2\\ &=\min_{y\in\C^n}\|(\underbrace{-y_1I-y_2A-\dots-y_nA^{n-1}+A^n}_{p_n(A)})b\|_2\\ &=\min_{\substack{p_n\in P_n\\p_n\text{ monic}}}\norm{p_n(A)b}_2. \end{aligned} \]